
- Overview
- Arista ™ AH Absorbable Hemostat
- Avitene™ Microfibrillar Collagen Hemostat
Hemostatic Agents and How They Are Used
Hemostatic agents are substances to help prevent/stop bleeding from the bleeding site and involves the dependent reactions of plasma proteins, calcium ions and blood platelets which softens the platelet plug from the fibrinogen-to-fibrin conversion.
What are Topical Hemostatic Agents?
- Definition: As a subcategory of hemostatic agents, topical hemostatic agents are crucial as they help prevent excessive bleeding during surgery or trauma and aids to mitigate risks associated with bleeding complications. Topical hemostatic agents actively participate in coagulation making them an ideal hemostatic agent where oozing and/or small surgical procedural bleeds exist cases of blood oozing and/or small surgical procedures bleeds.
What is Arista ™ AH Absorbable Hemostat?
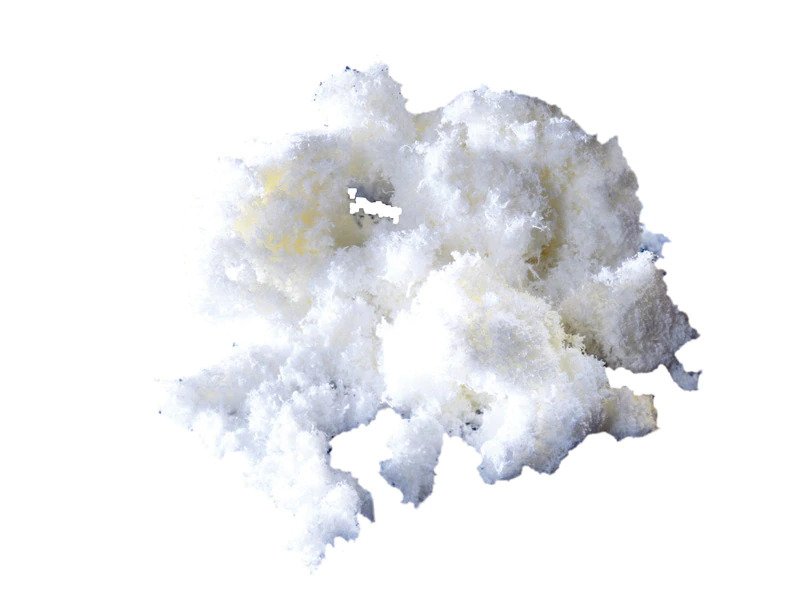
- Arista™ AH is a 100% plant-based absorbable hemostatic powder derived from purified plant starch.
- The power of Arista™ AH lies in its Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres, a patented blood clotting technology.
What are Examples of Hemostatic Agents?
Microporous Polysaccharide Hemispheres
Example: Arista™ AH Absorbable Hemostat
The MPH™ particles concentrate blood solids such as platelets, red blood cells and blood proteins to form a gelled matrix. By providing a barrier to further blood loss, the normal clotting process is enhanced, regardless of the patient’s coagulation status. This hemostat can be used in the following surgeries:
- Cardiothoracic and cardiovascular
- Vascular
- Gynecological
- Urology
- Orthopedic surgery
- General surgery
- Plastic surgery
- Ear, nose and throat (ENT)surgeryNN
Avitene™ is approved for use for use in all procedures where a topical hemostat is indicated, including neurosurgery.
Hemostatic Dressings Definition and How They Work:
Hemostatic dressings are a crucial supplement in regards to external hemorrhage control when bleeding site is not salvageable. The 3 hemostatic dressing gauze’s (combat, celox, chito) are applied similarly. When using hemostatic dressings, place entire dressing firmly and carefully over area of active bleeding site. When the dressing is all packed into wound, hold pressure there for 3-5 minutes. Keep in mind the importance of overpacking wound with enough hemostatic dressing so when estatic pressure dressing is applied, it will adjunct pressure of previous action.
Thrombin Definition and How They Work:
“Thrombin is a Na+ -activated, allosteric serine protease that plays opposing functional roles in blood coagulation”(NCBI). Thrombin works by acting as a procoagulant factor when it converts fibrinogen to fibrin. As a result, a stable fibrin clot is formed. Fibrin works as scaffold for platelets when it became crosslinked.
Oxidized cellulose
Oxidized cellulose, also known as a treated surgical gauze, comes in many forms (strips, gauze pads, pledgets). It works, acting like a physical matrix to form clots while not actively causing alterations of clotting cascade. Oxidized cellulose is usually removed after coagulation, but can be left on surgical site.
Absorbable Gelatin Sponge:
Absorbable Gelatin Sponge (Gelfoam) is a gelatin powder that is applied dry to wound with light pressure. The absorbable gelatin allows for clot formation and forms granulation tissue while holding the blood. Gelfoam aids in forming bulky artificial clot in vascular areas to stop further bleeding.
Hemostatic Agents in Surgery:
Hemostatic hemostasis in surgery are a crucial element to the achievement of a positive outcome. Along with maintenance of homeostasis of the patient during surgery or trauma, it also provides many benefits such as reduction time in hospital stay, number of redo interventions for bleeding, reduce surgery time, intra- and postoperative complication rate and high economic efficiency. When selecting a hemostat for surgical practice, it is important doctors keep in mind the accessibility of bleeding site, size of wound, and the type of agent. In addition, they should take into account the severity of the bleed, patient’s coagulation status, patient’s medical or surgical history, and likelihood of reoperation when choosing agent and identification of bleeding risk.
What are the Advantages of Using a Hemostatic Agent?
Benefits of using a hemostatic agent in surgery and in emergency situations include maintenance of the patient’s hemostasis. Potential benefits encompasses shorter operation duration, reduction in transfusion requirement, greater management of anticoagulated patient, reduction in patient recovery time, reduce intra- and postoperative complication rate and a reduction in wound exposure.
Hemostatic Agent
What Happens During Hemostasis?
Hemostasis includes the following steps:
- Vascular Spasm or Vasoconstriction
- Platelet formation
- Clot formation/ Blood Coagulation
How Does a Hemostatic Agent Work?
When control of capillary, venous, and arteriolar bleeding by pressure, ligature, and other conventional procedures is ineffective or impractical, hemostatic agents are introduced and work either mechanically or by augmenting the coagulation cascade in order to stop the bleeding. The purpose of a hemostatic agent is to maintain hemostasis of the patient during surgery or trauma.
Why are Hemostatic Agents Used?
Without hemostatic agents, operating times may need to be prolonged and the risk of side effects increases.
- In a 2015 clinical study regarding efficacy of Arista™ AH, it was proven that full hemostasis of first treated lesion within 5 minutes (3 minutes for cardiac procedure) results in a success rate of 94.4%, 78.9%, and 94.3% in general, cardic, and orthopedic procedures.
Hemostatic agents can also help to decrease risk in emergency cases such as trauma. Hemorrhagic shock is the second leading cause of death for civilian trauma patients.
When are Hemostatic Agents Needed?
- Hemostatic agents are often needed in surgical procedures when bleeding cannot necessarily be avoided.
- They are also often needed in emergencies where bleeding needs to be controlled.
What are the Subtypes of Hemostatic Agents
There are three main subtypes of hemostatic agents:
- Caustic: Caustic hemostatic agents work by coagulating proteins leading to tissue necrosis and eschar formation, which strengthens the formation of thrombus and hemostasis.
- Physical: Physical hemostatic agents use a substrate (cellulose, gelatin, starch, collagen) which forms a matrix at bleeding site. Extrinsic coagulation cascade is then activated by the dependent reactions of plasma proteins, calcium ions and blood platelets softening that platelet plug from fibrinogen-to fibrin conversion, thus serving as a platform to form clots.
- Biologic: Biologic hemostatic agents, include topical thrombin and fibrin sealants, which promote hemostasis from the bypass of initial steps of coagulation cascade (extrinsic pathway).
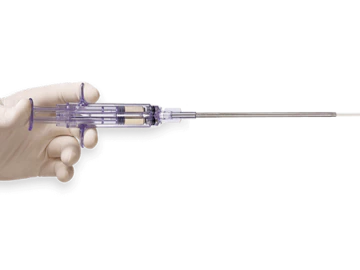
- Topical thrombin agents are applied with either a syringe or spray and should not be combined with oxidized regenerated cellulose since this acidity may neutralize topical thrombin effectiveness.
- Fibrin sealants enable fibrin clot to form when applied directly to site of bleeding. It is made of thrombin solution and concentrated human fibrinogen solution.
Are you Using BD Hemostatic Agents?
How you use a hemostat will depend on the type of bleeding. Below are directions for two common types:
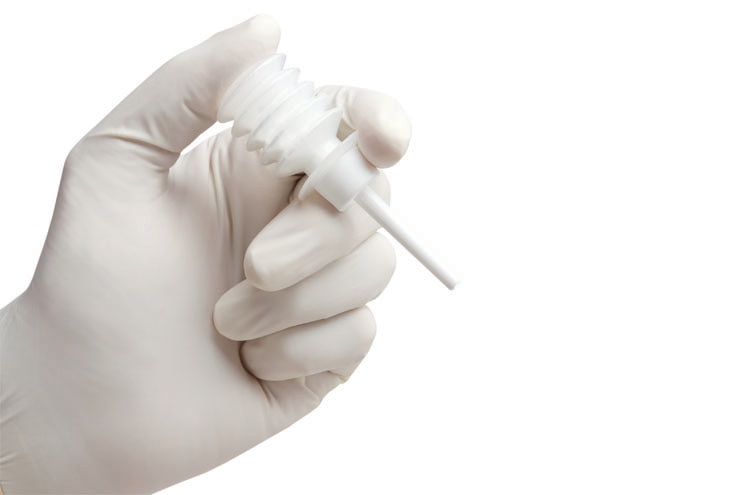
Microporous polysaccharide hemispheres (Arista™ AH):
- Blot, wipe, or suction the bleeding tissue. It is important to remove excess blood so that Arista™ AH maybe applied immediately and directly to the site of active bleeding.
- Immediately apply a liberal amount of Arista™ AH at the site of bleeding within the wound, as close to the source of bleeding as possible, completely covering the wound. Deep wounds may require equally deep application of Arista™ AH. To minimize occlusion of the tip, pressure should be applied to deliver Arista™ AH as the applicator enters the wound.
- Quickly apply wound-appropriate, direct pressure over the treated site; use of a non-adhering substrate to apply pressure may prevent adhesion of the formed clot to the surgical glove or other instrumentation. Amount and duration of pressure is wound dependent. For neurological applications, pressure is not recommended and for oozing, pressure may not be necessary. For more profuse bleeding wounds, pressure should be maintained longer.
- If bleeding or oozing continues, remove excess Arista™ AH and reapply.
- If any material (ie, surgical glove, sponge, etc) adheres to the newly formed clot, irrigate the material with saline and carefully remove it from the treated site
- Immediately upon contact with fluid, Arista™ AH will swell to approximately 5 times its original volume. Once Hemostasis is achieved, excess Arista™ AH should be carefully removed by irrigation and aspiration.
Microfibrillar Collagen Hemostat (Aviente™):
AVITENE™ (MCH) must be applied directly to the source of bleeding. Because of its adhesiveness, it may seal over the exit site of deeper hemorrhage and conceal an underlying hematoma as in penetrating liver wounds. When possible, surfaces to be treated should be compressed with dry sponges immediately prior to application of the dry AVITENE™. It is then advantageous to apply pressure over the AVITENE™ with a dry sponge for a period of time which varies with the force and severity of bleeding. A minute may suffice for capillary bleeding (e.g., skin graft donor sites, dermatologic curettage) but three to five or more minutes may be required for brisk bleeding (e.g. splenic tears) or high pressure leaks in major artery suture holes. For control of oozing from cancellous bone, it should be firmly packed into the spongy bone surface. After five to ten minutes, excess MCH may be teased away (see Precautions); this can usually be accomplished with blunt forceps and is facilitated by wetting with sterile 0.9% saline solution and irrigation. If breakthrough bleeding occurs in areas of thin application, additional AVITENE™ may be applied…. In neurosurgical and other procedures the non-woven web may conveniently be used by applying small squares to bleeding areas and then covering the sites with moist cottonoid “patties””. After five to ten minutes excess MCH may be removed by teasing and irrigation.
What is Arista ™ AH Absorbable Hemostat?
- Arista™ AH is a 100% plant-based absorbable hemostatic powder derived from purified plant starch.
- The power of Arista™ AH lies in its Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres, a patented blood clotting technology.
Easy to Use:
- Arista™ is ready on-demand with a 5 year shelf life.
- No mixing and no refrigeration are required.
- Arista™ provides broad area coverage on rough surfaces and in hard-to-reach areas.
Thrombin-Free and 100% Plant-Based
- Thrombin-free, biocompatible and non-pyrogenic.
- Arista™ is 100% plant-based.
Faster Hemostasis
- Complete Hemostasis is achieved in minutes.
- The clotting process begins on contact, regardless of a patient’s coagulation status.
- Typically absorbed in 24-48 hours* by amylases.
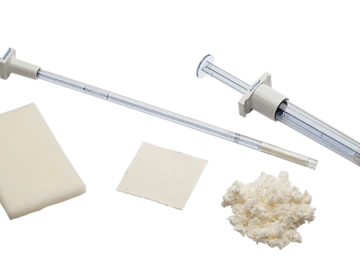
What is Avitene™ Microfibrillar Collagen Hemostat?
Avitene™ Microfibrillar Collagen Hemostat is an active absorbable collagen hemostat, proven to accelerate clot formation. Avitene™ effectively enhances platelet aggregation and the release of proteins from the blood to form fibrin, resulting in hemostasis.
100% Collagen
- Every product in the Avitene™ MCH family of hemostats is made from 100% collagen, which is proven to accelerate clot formation across surgical specialties.
Trusted For Over 40 Years in 50 Countries
- Avitene™ MCH is made in the United States, and is trusted by surgeons across the globe.
- Avitene™ MCH has been trusted by surgeons for its safety and efficacy for over 40 years.
Five Versatile Formats
- Acceptable for use in all procedures where a topical hemostat is indicated, including neurosurgery. Avitene™ MCH’s five formats provide versatile options to fit each specific procedure.
Thrombin-Free and Patient Savings
- Avitene™ MCH is ready to use out of the package.
- Reduced dependence on thrombin equals better health economics and reduced costs for patients.
BD-68609